Variables
A variable is a “cell” in memory that stores data. The data in a variable is its value.
You can:
- Declare variables and assign values to them.
- Refer to variables.
- Send variable values to clients.
- Replace part of a variable.
- Get client data from publication channels via a system variable.
You can store the client name, the response from the server, data from the database, etc. in a variable. To use this data in the script, you just need to refer to a variable.
What variables Aimylogic has
Aimylogic has auto-generated system variables and user-defined variables that you can create.
How to create a variable
To create a variable, you can:
- Declare it via the Conditions block.
- Save data from the client.
- Save the result of the last client’s input.
- Save the result of the HTTP request.
Declare a variable via the Conditions block
To create a variable, add the Conditions block and specify a JavaScript expression to assign a value to a variable — for example, a number, a string, or a value of another variable.
Save data from the client
With the text to $var, num to $var, and file to $var blocks, you can store text, a number, or a file in a variable.
When using one of these blocks, you need to specify a name for the variable the data will be saved to.
Save the result of the last client’s input
When a client writes or says something that is recognized by some intent, the whole client’s phrase is saved to the $queryText system variable.
When another intent recognizes a new client’s input, the data in the $queryText variable is overwritten.
If you want to save a particular client’s input and have an access to it in the script, you can assign the $queryText value to a new variable via the Conditions block:
The script example:
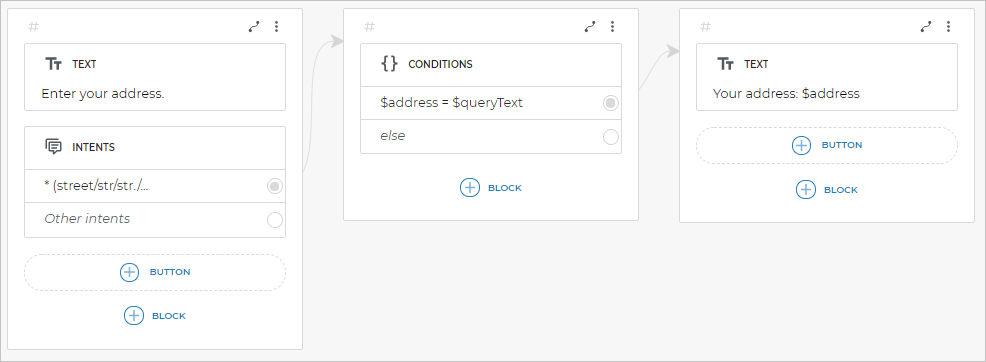
The chat example:
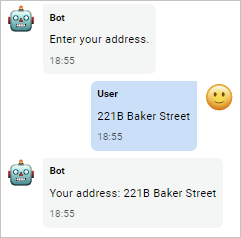
Save the result of the HTTP request
Aimylogic automatically saves the result of the HTTP request to the $httpResponse system variable.
When a new request is executed, the data in the $httpResponse variable is overwritten.
If you want to keep data of a particular request, you can assign the $httpResponse value to a new variable via the HTTP request block
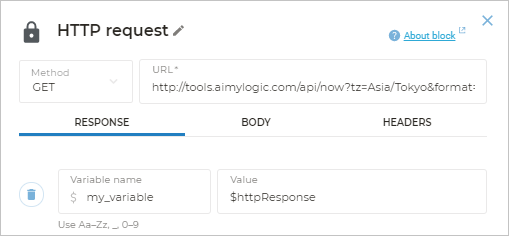
How to name a variable
A variable should always have a name so that the bot can refer to it in the script.
When you declare a variable, you specify its name. System variables have their own reserved names.
A variable name:
- Can contain numbers, Latin characters of any case, and underscores.
- Should start with a letter.
- Must not match the JavaScript reserved words.
To add a variable to a condition or refer to it in a script, write its name with $ in front of it: $variable_name.
When you create a variable via one of the blocks from the Extended capabilities section or via the HTTP request block, you do not need to add $ in front of the variable name.
How to use variables
To use a variable you have created before, add $ in front of its name, for example:
$client_number
Add to conditions
You can use variables in the Conditions block to make the bot select a script branch depending on the condition that is fulfilled first.
For example, for your bot to receive a number from the client, compare it with another one, and follow the branch depending on the result:
Add the Conditions block to the script.
Add the necessary JavaScript expressions to make the bot compare the variable value with another one. It can be a number or another variable containing a number.
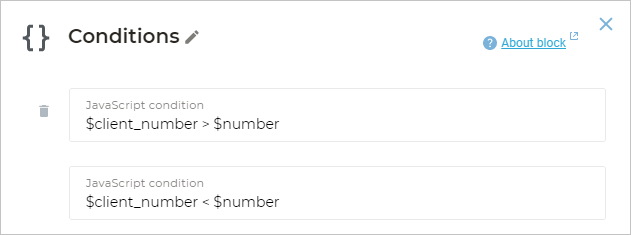
Connect each condition with a new screen.
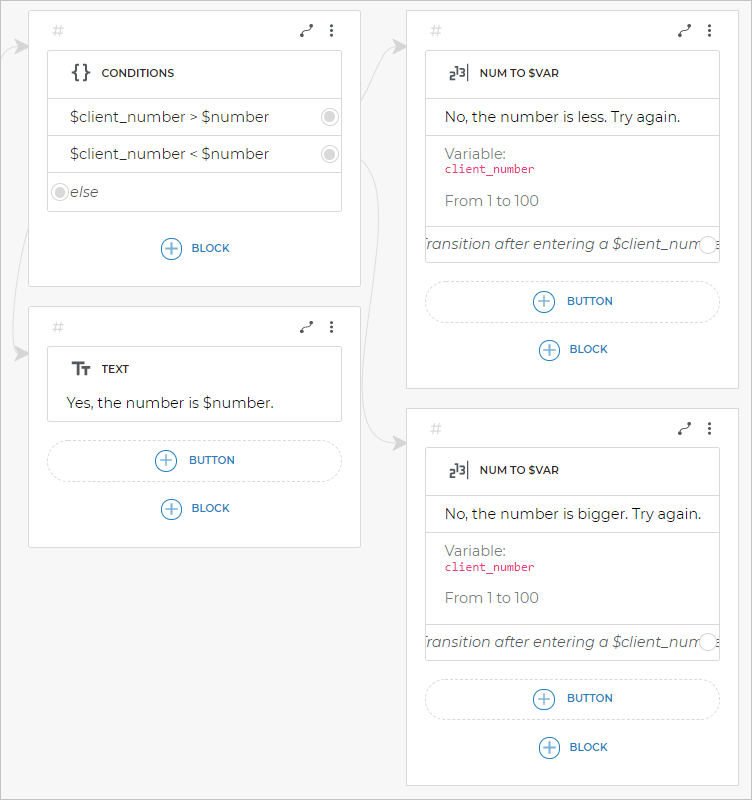
Depending on the comparison results, the bot will go to a particular screen.
Add to the text
You can add the value of any variable to the message text. To do this, when editing the Text block, add the variable name with $ in front of it:
In the message the client receives from the bot, the variable name will be automatically replaced with its value.
For example, if the client guesses the number stored in the $number variable that is equal to 5, the client will receive the following message: Yes, the number is 5.
Add to the HTTP request
To send data to a third-party server or make a dynamic request, you can add variables to the request.
